EPDM Membrane
EPDM ( Ethylene-Propylene-Dien-Monomer ) is a 100% vulcanized synthetic monolayer membrane in epdm films of varying thicknesses, chemically stable with practically unlimited UV and Ozone resistance. Contains no plasticizers.
For the past 50 years since the first EPDM rubber membrane was installed , billions of square meters have been installed worldwide for various applications from roof roofs to pools for water storage.
For the past 50 years since the first EPDM rubber membrane was installed , billions of square meters have been installed worldwide for various applications from roof roofs to pools for water storage.
No other waterproofing membrane has succeeded in approaching or matching the longevity requirements, which is why the use of EPDM increases exponentially every year.
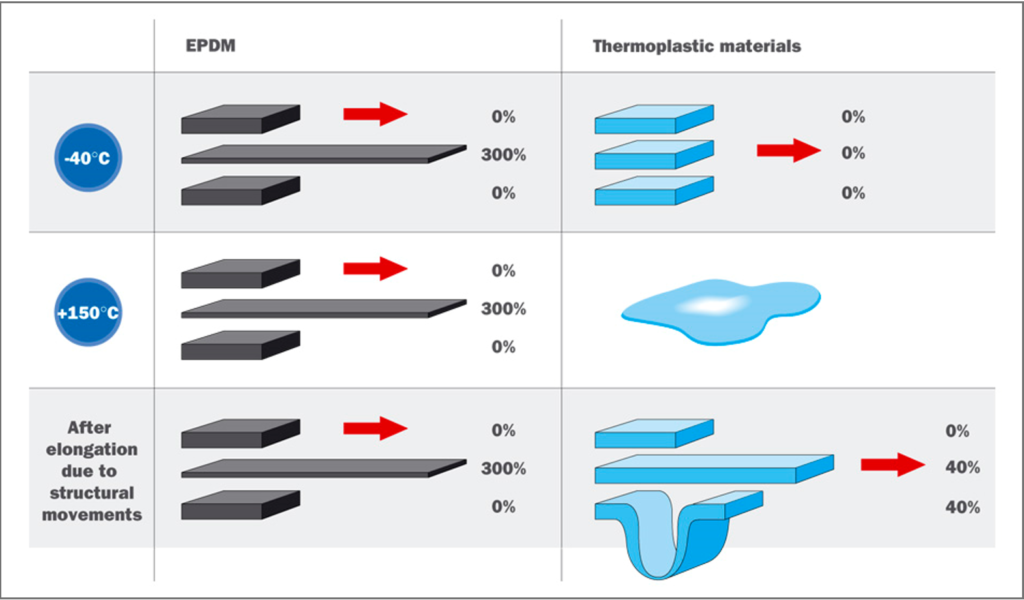
The exceptional elongation of over 300% is also a parameter that gives EPDM the advantage of taking over mechanical stresses as no other material can. EPDM waterproofing systems are flexible systems capable of absorbing the dimensional changes of the support they have been applied, modifications generated by constructive defects, uneven settlements or landslides.
EPDM membrane waterproofing systems can be used and installed in any type of climatic conditions, maintaining flexibility up to -40°C.
- CE certification
- DIN EN ISO 9001: 2000 quality assurance system
- Temperature resistant -45°C to 130°C
- Contains no chlorine, plasticizers, halogens and heavy metals
- Resistant to ozone and UV radiation
- Resistant to ozone and UV radiation
- Approval for drinking water, does not contain talc
- Resistant to root penetration
EPDM vs HDPE
Waterproofing membranes are produced by different methods, using a wide variety of raw materials: resins, additives, carbon black … The expected result is an economical membrane, easy to install and very durable.
However, the differences between membranes are significant and should be studied in detail before recommending them for a particular use.
The two membranes currently designed and used for outdoor exposure are EPDM rubber membrane and HDPE thermoplastic.
What follows is a brief comparative analysis between EPDM and HDPE.
The EPDM membrane is made from a synthetic rubber composed of isobutyl and isoprene (IIR) with excellent resistance to external factors, chemical agents and UV radiation.
HDPE is a semi-crystalline thermoplastic compound that has also been designed for outdoor exposure. However, considering its semi-crystalline structure it is sensitive to premature cracking and especially to cracking under stress conditions (cracking as a result of stresses); Welding areas are particularly vulnerable, areas that are facing more important thermal variations. Stress cracking transforms HDPE into a fragile material.
The EPDM membrane waterproofing system maintains its physical and chemical properties (elasticity) between – 45 ° C and 130 ° C, remaining unaffected until an induction of 250 ° C.
Being a semi-crystalline HDPE polymer it has a higher thermal conductivity so that at low temperatures it causes a rigidity of the material adding a dangerous voltage to the membrane.
Being an EPDM elastomer , it is elastic, returning to its initial position after an elongation effort.
Thermoplastic materials (like HDPE) after repeated elongation do not return to their original shape, their deformation being permanent. After the 10-15% HDPE threshold it is no longer elastic.
The EPDM membrane is elastic, with elongations of up to 400% -500%.
This exceptional flexibility of the EPDM allows easy installation of the membrane that is perfectly modeled on the support, while the rigidity of the HDPE does not allow this adaptation.
HDPE has a high coefficient of expansion. By expanding at high temperatures it forms folds and malformations that can affect welds.
Currently the technical regulations require that the minimum thickness applicable to HDPE membranes be higher than the minimum thickness required in EPDM , precisely to compensate for the disadvantages of HDPE mentioned above.
EPDM Vs. PVC
Durability and aging:
EPDM is a synthetic rubber that due to its chemical structure has an excellent behavior in extreme climatic conditions and at the same time, it is not attacked by micro-organisms.
PVC is originally a rigid material. To become flexible it is added plasticizers (PVC-P), which over time migrate (evaporate) from the membrane generating its degradation and loss of mechanical properties.
Moreover, PVC is sensitive to heat, UV radiation and microorganisms.
The 0.5mm 0.75mm PVC foil or cannot be left outdoors without any protection, as it will suffer premature aging.
Also the acidity of the land where it is installed can be an aggressive factor for the PVC membrane, which is why it is necessary to carry out a study when it is desired to use it.
Temperature range:
The EPDM membrane maintains its physical and chemical properties constantly between -50 ° C and up to 130 ° C.
PVC is not resistant to low temperatures, it becomes rigid and can be very difficult to install, even with the risk of cracks occurring.
Hardness:
The EPDM membrane has a high elongation resistance => 400%, and is a product easy to install on any type of surface, regardless of the shape and irregularities of the substrate.
PVC is fragile when it comes to an irregular support layer and usually requires the use of a protective geotextile, which raises the price of the project.
